By: Mansour Baker | Posted: 17 January 2020
|
What is Employee Turnover?
|
Employee Turnover Multistage Process
|
Employee Turnover is a multistage process, the decision to stay or leave an organization begins with a person’s perception regarding how satisfied he or she is with the current position. The more satisfied employees are, the less likely they are to leave the organization.
1st Stage: The level of commitment and satisfaction an employee feels towards the organization. If employees are highly committed to the company’s goals and values but are not satisfied with their present position, they are more likely to seek opportunities within the organization, as opposed to outside.
2nd Stage: In this stage the employee starts to think about leaving his or her current job because of dissatisfaction with various aspects of the job or organization. 3rd Stage: The employee starts to search for alternative employment. The more frustration an employee experiences with the current role, the greater chance an employee will search for another position. 4th Stage: The employee starts to compare alternatives with the present job and decides. The more the employee searches for employment elsewhere, the more probable his or her leaving. 5th Stage: The employee is in the process of leaving to a new opportunity or actual staying. An employee may acquire additional information concerning the new opportunity that may affect the decision to stay or leave. Influencing employee turnover decision can best be focused on signs or symptoms of employee dissatisfaction and address the issue as it is evolving instead of waiting until the employee has decided to leave and gives formal notice period.
|
|
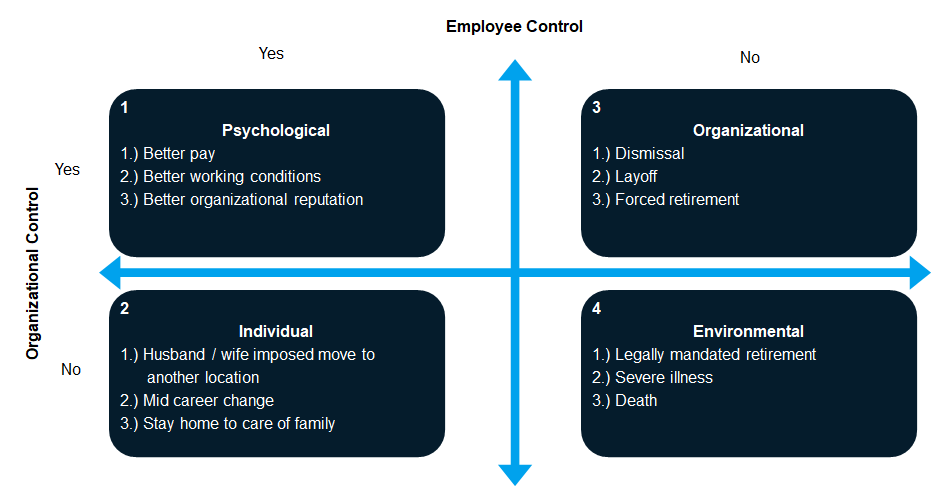
Exhibit 1
Not all employees progress through the turnover process the same way.
|
|
Functional Versus Dysfunctional Turnover
In some instances, turnover may increase organizational effectiveness. The departure of poorly performing staff will be Functional for the organization if they can be replaced by employees who are more competent.
Functional Turnover
Dysfunctional Turnover
|
|
Employee Turnover Audit Training
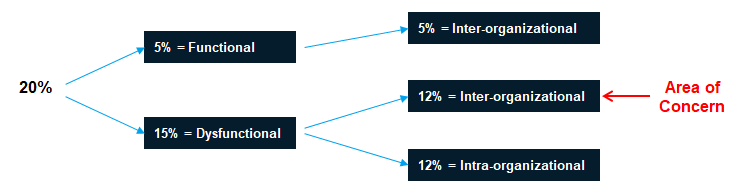
The 1st step is to determine the total percentage. The 2nd step is to identify high performers versus low performers. The 3rd step is to analyze the number of competent employees leaving the organization. This information will be used by the organization to evaluate and modify their workplace practices.
1st step is to determine the turnover rate during a specified period. The number of employees leaving are 20 and the total number of employees are 100 during a 12-month period. Divide the total number of people leaving by the total number of employees.
2nd step of the turnover audit is to determine what percentage of this turnover is dysfunctional & functional. 15 employees are high performers and 5 employees are low performers or troublemakers.
3rd step of the turnover audit is to determine what percentage is inter-organizational & intra-organizational employee movements.
|